Insights regarding mitochondrial DNA copy number alterations in human cancer (Review)
The DNA copy numbers were estimated for each tissue based on four different rtPCR reactions: nuclear DNA, mitochondrial DNA, nuclear DNA diluted by 10, and mitochondrial DNA diluted by 10. Each rtPCR reaction was replicated 24 times, giving a total number of 4 × 24 = 96 (a complete 96 well plate) reactions.
Mitochondrial DNA copy number, ATP production, and ATPase gene... Download Scientific Diagram

Abstract. Mitochondrial DNA copy number (mtDNA-CN), a measure of the number of mitochondrial genomes per cell, is a minimally invasive proxy measure for mitochondrial function and has been associated with several aging-related diseases. Although quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) is the current gold standard method for measuring mtDNA-CN, mtDNA.
Mitochondrial DNA copy number is regulated by DNA methylation and demethylation of POLGA in stem

Mitochondrial DNA copy number (mtDNA-CN), a measure of the number of mitochondrial genomes per cell, is a minimally invasive proxy measure for mitochondrial function and has been associated with several aging-related diseases.. Although several other studies have explored the impact of DNA isolation protocol on mtDNA-CN estimation[14,38,39.
IJMS Free FullText Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number and Developmental Origins of Health and

Chong, M. et al. GWAS and ExWAS of blood mitochondrial DNA copy number identifies 71 loci and highlights a potential causal role in dementia. eLife 11 , e70382 (2022) Article Google Scholar
A singletube multiplex qPCR assay for mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number assessment

Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number is a critical component of overall mitochondrial health. In this chapter, we describe methods for simultaneous isolation of mtDNA and nuclear DNA (nucDNA), and measurement of their respective copy numbers using quantitative PCR.
mitochondrial dna biparental

This unit describes PCR-based methods to measure nuclear and mitochondrial DNA damage and copy number. Long amplicon quantitative polymerase chain reaction (LA-QPCR) is used to detect DNA damage by measuring the number of polymerase-inhibiting lesions present based on the amount of PCR amplification; real-time PCR (RT-PCR) is used to calculate.
Mitochondrial DNA Biological Science Help Blog Biochemistry Help Blog Molecular Biology

Mitochondria are involved in a number of diverse cellular functions, including energy production, metabolic regulation, apoptosis, calcium homeostasis, cell proliferation, and motility, as well as free radical generation. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is present at hundreds to thousands of copies per ce.
Prognostic value of mitochondrial DNA content and G10398A polymorphism in nonsmall cell lung cancer
The forward and reverse primers for qPCR should have similar melting temperature (Tm). Design the Tm for qPCR primers around 62-72°C based on the formula, 4 (G + C) + 2 (A + T). The annealing temperature is determined by the lowest Tm of a primer set. The size of the amplicon is kept at around 60-150 bp.
Mitochondrial DNA copy number in blood of healthy controls and... Download Scientific Diagram

Abstract. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number is a critical component of overall mitochondrial health. In this chapter, we describe methods for isolation of both mtDNA and nuclear DNA (nucDNA) and measurement of their respective copy numbers using quantitative PCR. Methods differ depending on the species and cell type of the starting material.
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) Replication Mechanism, Factors

Alternatively, real-time PCR-derived mtDNA and nDNA copy number values can be used for normalization; see reference (Rooney et al., 2015) for real-time PCR protocol. Differences in mtDNA copy number between samples or treatments can obscure results, as it changes the amount of template DNA for the reaction.
Mitochondrial DNA copy numbers in genomic DNA isolated from groups of... Download Scientific

Background Mitochondrial genome copy number (MT-CN) varies among humans and across tissues and is highly heritable, but its causes and consequences are not well understood. When measured by bulk DNA sequencing in blood, MT-CN may reflect a combination of the number of mitochondria per cell and cell-type composition. Here, we studied MT-CN variation in blood-derived DNA from 19184 Finnish.
Mitochondrial DNA copy number analysis and mitochondrial transmembrane... Download Scientific

Mitochondrial DNA copy number (mtDNA-CN), a measure of the number of mitochondrial genomes per cell, is a minimally invasive proxy measure for mitochondrial function and has been associated with several aging-related diseases.. Although several other studies have explored the impact of DNA isolation protocol on mtDNA-CN estimation[14,38,39.
Estimated mitochondrial (mt) DNA copy numbers among isolates of E.... Download Scientific Diagram

However, the large majority of protocols assess the relative mtDNA copy number as a ratio between mtDNA levels and levels of a selected nuclear gene, which makes comparison between studies very difficult.. (2014) Association of leukocyte mitochondrial DNA copy number with colorectal cancer risk: results from the Shanghai Women's Health.
Mitochondrial DNA copy number, integrity and complex activity. a... Download Scientific Diagram

Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) copy number is a critical component of overall mitochondrial health. In this chapter we describe methods for isolation of both mtDNA and nuclear DNA (nucDNA), and measurement of their respective copy numbers using quantitative PCR.. Follow the Qiagen 20/G Genomic Tips Tissue protocol for DNA isolation. 3.1.3 Cell.
Mitochondrial DNA copy number in human disease the more the better? Filograna 2021 FEBS

DNA isolation protocol effects on nuclear DNA analysis by microarrays, droplet digital PCR, and whole genome sequencing, and on mitochondrial DNA copy number estimation. PLoS One 12 , e0180467 (2017).
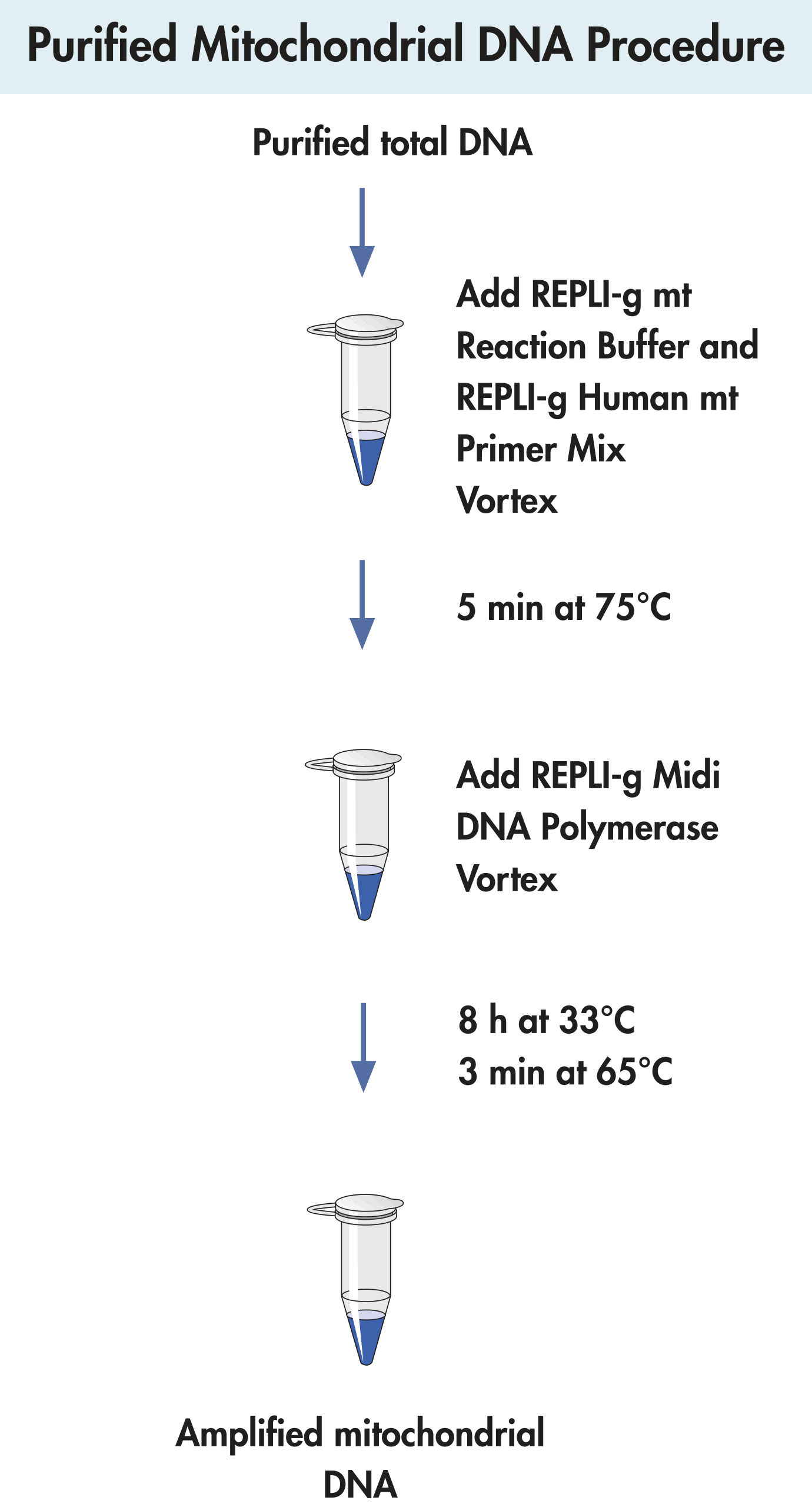
REPLIg Mitochondrial DNA Kit
This chapter provides protocols for the simultaneous isolation of mitochondrial and nuclear DNA, and measurement of both genome copy numbers from a variety of species. We present two protocols for copy number determination: real-time and non-real-time qPCR. They differ based on availability and optimization of reagents.