Medial geniculate nucleus of Thalamus Neuroanatomy YouTube

Abstract. The midline and intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus form a major part of the "limbic thalamus;" that is, thalamic structures anatomically and functionally linked with the limbic forebrain. The midline nuclei consist of the paraventricular (PV) and paratenial nuclei, dorsally and the rhomboid and nucleus reuniens (RE), ventrally.
[Figure, Thalamic nuclei Image courtesy S Bhimji MD] StatPearls NCBI Bookshelf

The intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus play a pivotal role in awareness, conscious experience, arousal, sleep, vigilance, as well as in cognitive, sensory, and sexual processing. Nonetheless, in.
Thalamus Anatomy, Location, Structure, Function & Physiology

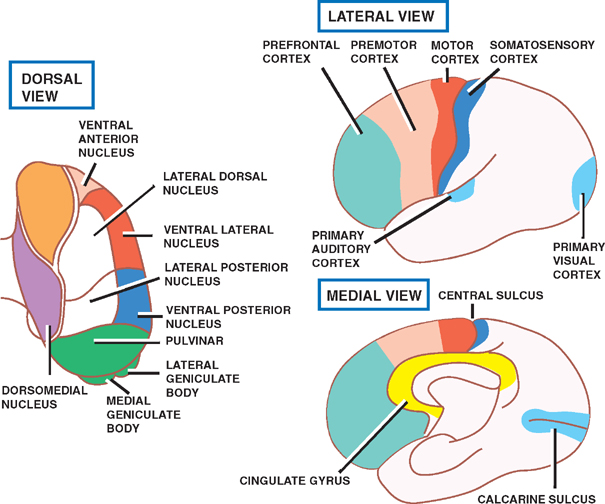
The intralaminar and medial thalamic nuclei are part of the higher-order thalamus, which receives little sensory input, and instead forms extensive cortico-thalamo-cortical pathways. The large mediodorsal thalamic nucleus predominantly connects with the prefrontal cortex, the adjacent intralaminar nuclei connect with fronto-parietal cortex, and the midline thalamic nuclei connect with medial.
Thalamus Anatomy
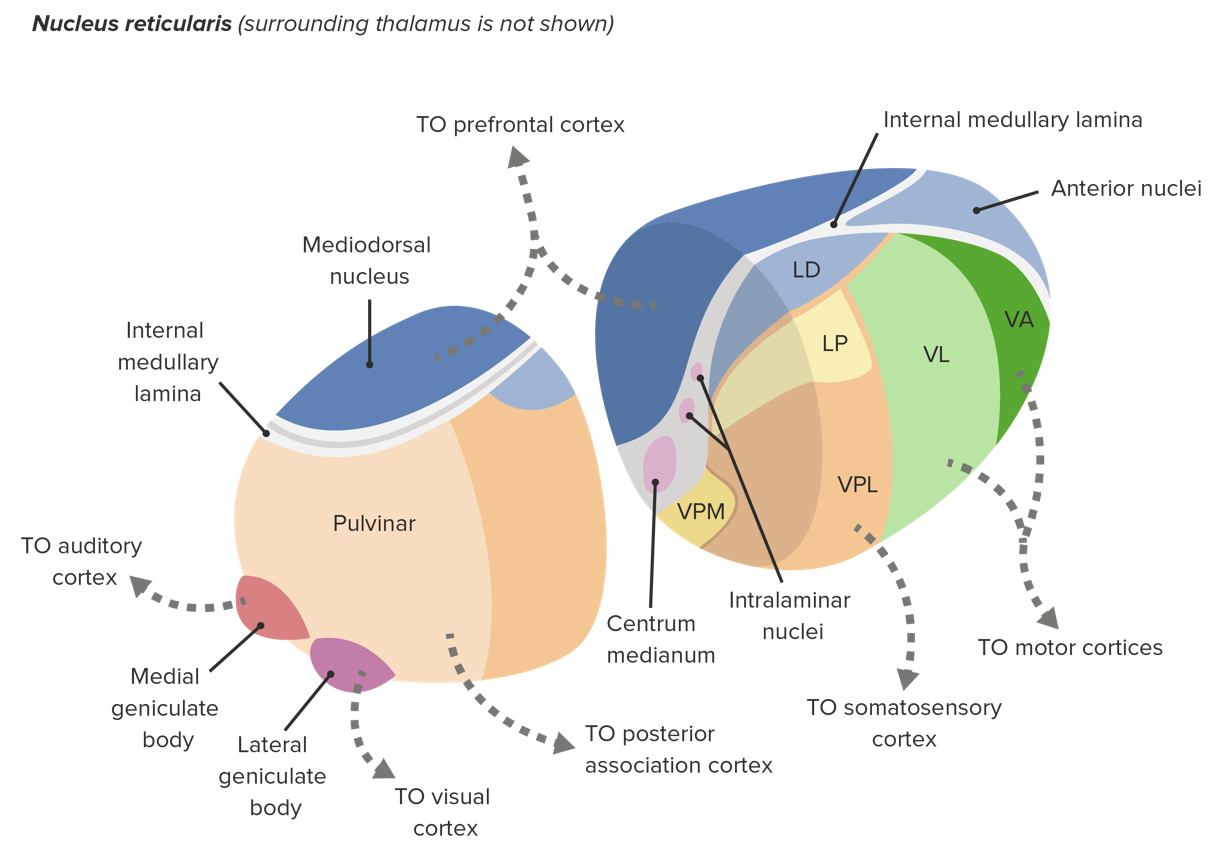
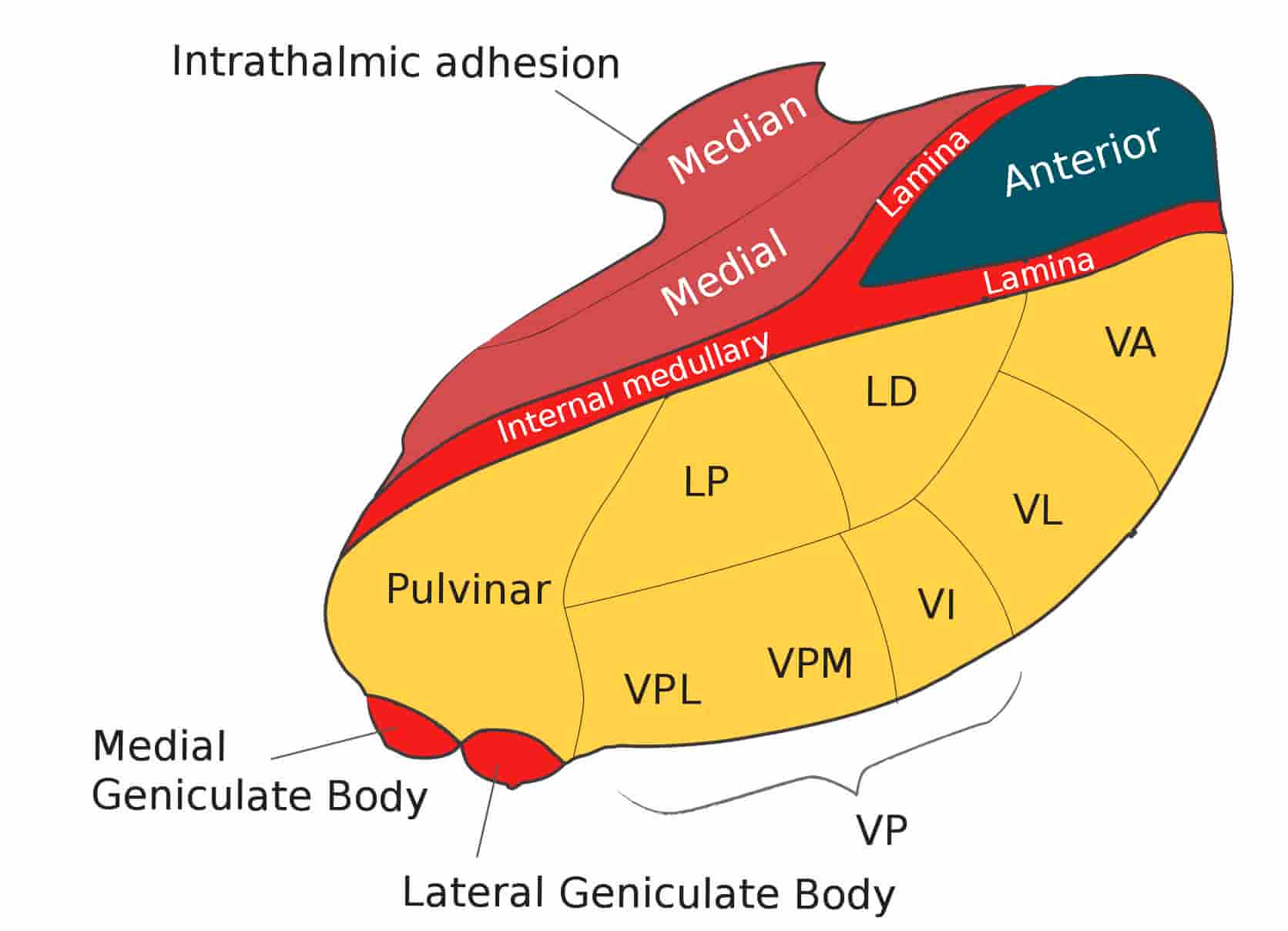
The thalamic nuclei are the clusters of densely packed neuronal cell bodies that comprise the thalamus. The thalamus is an ovoid, paired gray matter structure, found in the center of the brain, just superior to the brainstem. Each side of the thalamus contains six groups of nuclei; Anterior nuclei of thalamus. Lateral nuclei of thalamus.
Thalamic Nuclei Anatomy Diagram Quizlet

The midline and intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus form a major part of the "limbic thalamus;" that is, thalamic structures anatomically and functionally linked with the limbic forebrain. The midline nuclei consist of the paraventricular (PV) and paratenial nuclei, dorsally and the rhomboid and nucleus reuniens (RE), ventrally. The rostral intralaminar nuclei (ILt) consist of the central.
The Thalamus and Cerebral Cortex (Integrative Systems) Part 2 Neurology, Cerebral cortex

The intralaminar thalamic nuclei are located lateral to the mediodorsal nucleus and "embedded" within the internal medullary lamina. As previously indicated, the intralaminar nuclei are divided into a rostral and caudal division, with the rostral group consisting of the central medial (CM), paracentral (PC), and central lateral (CL) nuclei.
THALAMUS New
The intralaminar thalamic nuclei ( ITN) are collections of neurons in the internal medullary lamina of the thalamus that are generally divided in two groups as follows: [1] Some sources also include a "central dorsal" nucleus. Degeneration of this area can be associated with progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson's disease. [2]
Categories of Thalamic Nuclei Association, Reticular and Intralaminar Nuclei Diagram Quizlet

The intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus play a pivotal role in awareness, conscious experience, arousal, sleep, vigilance, as well as in cognitive, sensory, and sexual processing. Nonetheless, in humans, little is known about the direct involvement of these nuclei in such multifaceted functions and their structural connections in the brain.
Thalamus Neupsy Key
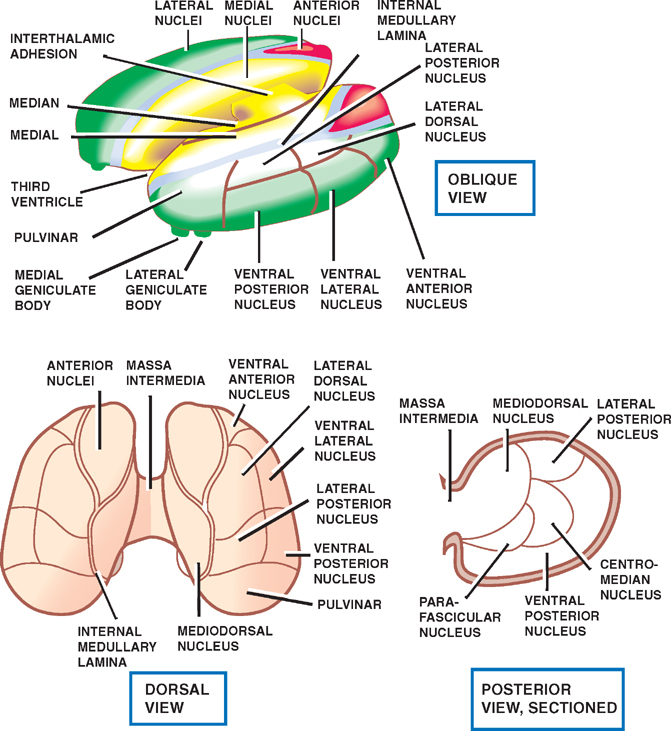
The thalamus serves as the main relay station for the brain. Motor pathways, limbic pathways, and sensory pathways besides olfaction all pass through this central structure. The thalamus can divide into approximately 60 regions called nuclei.[1] Each nucleus has unique pathways as inputs and various projections as outputs, most of which send information to the cerebral cortex.
Anatomy Of The Thalamus Anatomical Charts & Posters

The thalamic intralaminar nuclei and the cerebral cortex. In: Jones EG, Peters A, editors. Cerebral cortex. Vol. 5. New York: Plenum Press 1986;355-389. Crossref. Google Scholar. 17. Berendsc HW, Groenwegen HJ. Restricted cortical termination fields of the midline and intralaminar thalamic nuclei in the rat.
Thalamic nuclei Connections, functions and anatomy Kenhub
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/699/dEI9mLMVmJ5QEO4mOkUjzQ_thalamic-nuclei_english.jpg)
All midbrain candidate nodes connected with the intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus (IL) via DTT M and with PaV via VTT R (Figs. 2 and 4 and Table 1). All midbrain nodes except the ventral. C. Caballero-Gaudes, P. M. Paz-Alonso, A probabilistic atlas of the human thalamic nuclei combining ex vivo MRI and histology. NeuroImage 183, 314-326.
Thalamus Functions Nuclei Connections AnatomyQA

The intralaminar nuclei of thalamus are a collection of nerve cells which are situated within the internal medullary lamina. They receive neuronal inputs from various pathways, however, the major input arises from the basal ganglia. They have two-way connections with the cerebral cortex.The intralaminar nuclei of thalamus can be subdivided into caudal and rostral sub-groups:The caudal.
Thalamus Neupsy Key
Together, the intralaminar and midline nuclei form a conspicuous arrangement of nuclei in the medial dorsal part of the rat thalamic complex (Fig. 1).The midline nuclei, as the name implies, are located medially in the thalamus as a thin strip of cells, spanning the entire dorsal-to-ventral extension of the thalamus.
Thalamus Nuclei Anatomy By rev.med Thalamus Nuclei GrepMed

There are smaller nuclei found in the internal medullary lamina known as the intralaminar nuclei and the midline nuclei. These nuclei receive inputs from the reticular formation. The former, however, also communicates with the trigeminothalamic and spinothalamic tracts, as well as other nuclei of the thalamus.
6. The development of the thalamus and its connections to the cortex in... Download Scientific
Together, the intralaminar and midline nuclei form a conspicuous arrangement of nuclei in the medial dorsal part of the rat thalamic complex (Fig. 1). The midline nuclei, as the name implies, are located medially in the thalamus as a thin strip of cells, spanning the entire dorsal-to-ventral extension of the thalamus.
The Parabrachial Nucleus Directly Channels Spinal Nociceptive Signals to the Intralaminar

The central thalamus (CT) comprises multiple intra- and paralaminar thalamic nuclei, which are interposed between the brainstem/basal forebrain arousal systems and the cortex ().Central thalamic neurons play a key role in arousal regulation through anatomical connections with large-scale cortical networks ().In their pioneering work, Moruzzi and Magoun stimulated the brainstem reticular.