PPT Chapter 7 Using Indicator Variables PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1948272

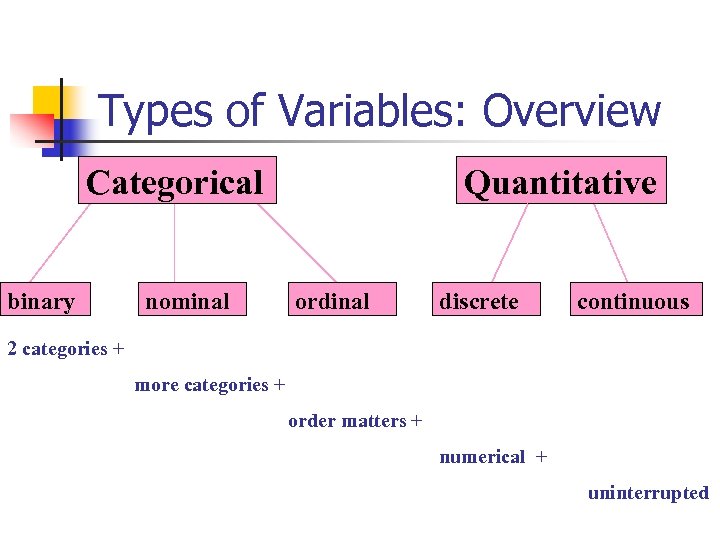
Indicator Variables. In general, the explanatory variables in any regression analysis are assumed to be quantitative in nature. For example, the variables like temperature, distance, age etc. are quantitative in the sense that they are recorded on a well-defined scale. In many applications, the variables can not be defined on a well-defined.
PPT Monitoring and Evaluation Indicators PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1429518
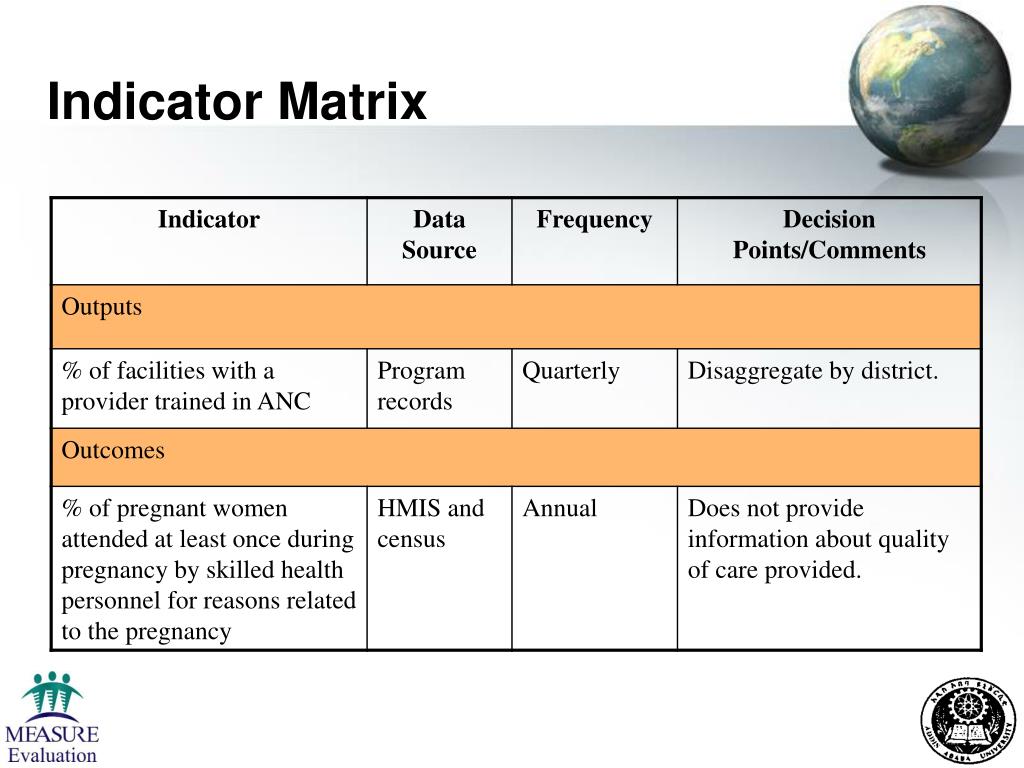
A useful tool for counting is an indicator variable: Definition: The indicator variable for an event \(A\) is a variable having value 1 if the \(A\) happens, and 0 otherwise. The number of times something happens can be written as a sum of indicator variables. In the coin example, we could define an indicator variable \(I_1\) which is 1 if the.
Research Variables and Research Indicators Download Scientific Diagram

This brief introduction explains how indicator random variables (or indicator functions) are defined in probability and statistics.
Looking at Data Clinical Data Example n
8.2 - The Basics of Indicator Variables. A " binary predictor " is a variable that takes on only two possible values. Here are a few common examples of binary predictor variables that you are likely to encounter in your own research: Gender (male, female)
Identifying Variables, Indicators, And Measures Attitude (Psychology) Likert Scale

11.3 Indicators in R. For a categorical variable (class is character or factor), R will automatically create the indicator variables.The category that comes first alphabetically is chosen as the reference category (unless a different reference is explicitly set for a factor variable.) The variables are given a name that is a combination of the variable name and the category label.
PPT Chapter 8 Regression Models for Quantitative and Qualitative Predictors PowerPoint
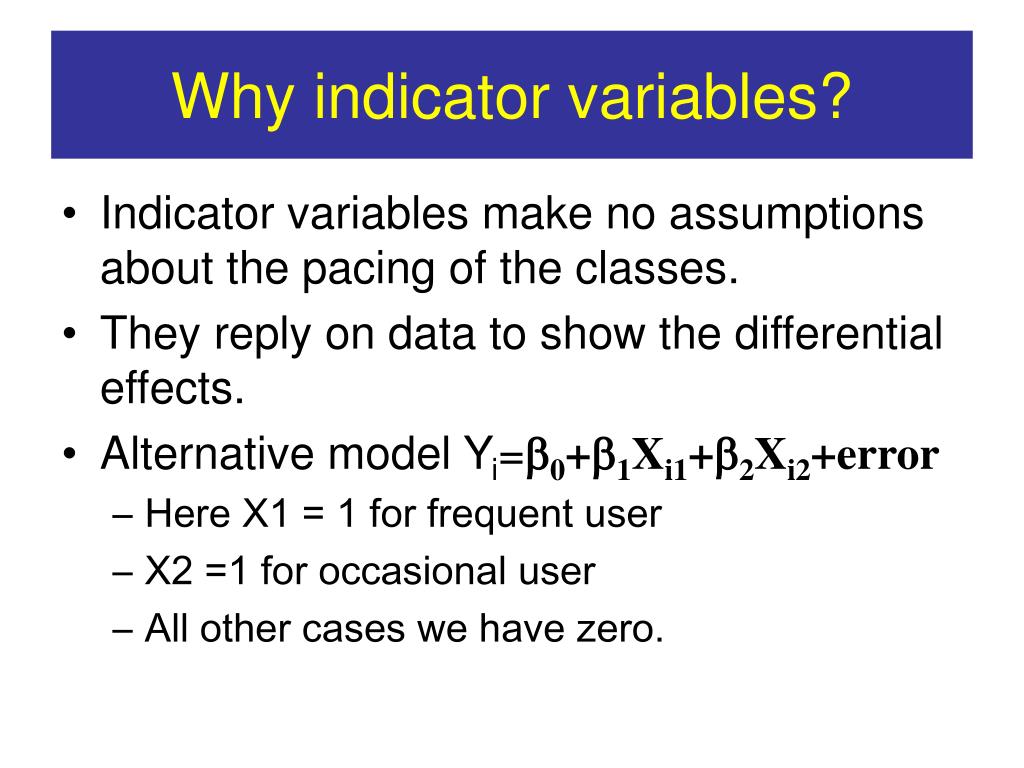
Model variable selection begins with the choice of potential drivers from logic and experience. The addition of indicators in the variable selection process is considered in this chapter. 7.1 Indicators Modify the Intercept to Account for Segment Differences To compare two segments, a 0-1 indicator can be added to a model. One segment becomes the
Introduction to the Variable Moving Average Technical Indicator YouTube

Indicator (statistics) In statistics and research design, an indicator is an observed value of a variable, or in other words "a sign of a presence or absence of the concept being studied". [1] Just like each color indicates in a traffic lights the change in the movement. For example, if a variable is religiosity, and a unit of analysis is an.
Week 10 INDICATOR VARIABLES YouTube

Variable means changeable and characteristic of something,. It may be number like 3, 5, 8 or a word like age, income, and expanse. Considering above definition in somehow it is also indicator. Measure means calculating some numbers or gauging some things. Index has close definition to indicator, some time we use it interchangeably.
PPT Indicator Variables PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4361782

Indicators are statistics used to measure current conditions as well as to forecast financial or economic trends. Economic indicators are statistical metrics used to measure the growth or.
Indicator Variables YouTube

In scientific research, concepts are the abstract ideas or phenomena that are being studied (e.g., educational achievement). Variables are properties or characteristics of the concept (e.g., performance at school), while indicators are ways of measuring or quantifying variables (e.g., yearly grade reports).
Indicator of research variables. Download Scientific Diagram

An indicator variable is a random variable that takes the value 1 for some desired outcome and the value 0 for all other outcomes. They indicate (hence the name) whether a subject belongs to a specific category or not. More specifically, an indicator variable X X is defined by. X = \begin {cases} 1 & \text {desired event} \\ 0 & \text {other.
probability Expected Value and Indicator Random Variable Cross Validated

Dummy variable (statistics) In regression analysis, a dummy variable (also known as indicator variable or just dummy) is one that takes a binary value (0 or 1) to indicate the absence or presence of some categorical effect that may be expected to shift the outcome. [1] For example, if we were studying the relationship between biological sex and.
Dimension, control variable, variables indicators and Issue of approach Download Scientific

Dummy Variables in Regression. A dummy variable (aka, an indicator variable) is a numeric variable that represents categorical data, such as gender, race, political affiliation, etc. Technically, dummy variables are dichotomous, quantitative variables. Their range of values is small; they can take on only two quantitative values.
Classification of Variables and Types of Measurement Scales YouTube

12.6 Indicator Variables. A special case of a variable with multiple categories is an indicator variable. These variables are sometimes referred to also as binary or dummy variables. You can think of these variables with just two categories: 0 and 1. Usually the level of 1 is reserved for the characteristic of interest.
Variable, Dimension, and Variable Indicator Download Scientific Diagram

An Indicator variable is a categorical variable that has exactly two levels. Logical variables are an example of an indicator variable. These are an important class of variables for many analyses where factor variable must be converted to a set of indicator variables. Indicators variables often use the values 0 and 1 for the two levels, but not.
PPT Variables PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2947388

A set of observed variables can "indicate" the presence of one or more latent (hidden) variables — hence the term indicator variable. Coding Categorical variables with multiple levels If you have a categorical variable with more than two levels (groups or levels are different groups in the same independent variable ), multiple dummy.